Understanding Communication
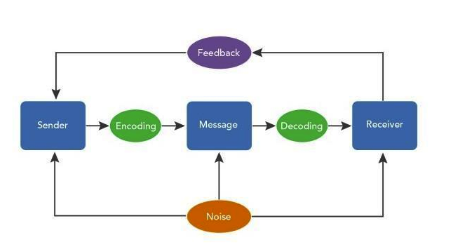
Communication is a vital part of our daily lives. It is a two-way process involving both the giving and receiving of information. We engage in communication in various forms throughout the day, often without even realizing it.
Some common examples include:
- Listening to teachers in school
- Reading books, newspapers, or magazines
- Talking with friends and family
- Watching television or using online platforms
- Addressing an audience during a conference or meeting
- Writing formal reports, newsletter articles, or emails
These examples highlight how communication can take place through verbal, nonverbal, written, and visual methods. Effective communication is essential in both personal and professional settings, as it helps convey information clearly, build relationships, and support collaboration.Demonstrating Knowledge of Various Methods of Communication for class 10
Different Forms of Communication
People communicate with each other in many ways every day — sometimes verbally, other times through written words, and often nonverbally through body language. Communication is not limited to just speaking; it involves a combination of methods. Experts suggest that communication consists of several key components: words, voice tone, and nonverbal cues such as gestures, facial expressions, and posture.
Each of these forms plays a different role in how effectively a message is delivered. In fact, nonverbal communication often conveys more meaning than words alone. Depending on the context, some methods of communication are more effective than others.
Overall, communication can be categorized into verbal, nonverbal, and written forms — each with its own purpose and impact.
Types of Communication
Communication can be broadly categorized into verbal and non-verbal forms.
Verbal Communication
Verbal communication refers to the form of communication in which a message is transmitted through spoken or written words. The primary goal of all communication is to ensure that the intended message is clearly understood by the receiver.
An important principle to remember in verbal communication is the acronym KISS — Keep It Short and Simple.
Verbal communication can be divided into two main types:
- Oral Communication – includes face-to-face conversations, phone calls, meetings, presentations, etc.
- Written Communication – includes emails, letters, reports, memos, and other written formats.
2. Non-Verbal Communication
Non-verbal communication involves conveying messages without the use of words. It includes a variety of elements that support, enhance, or even contradict verbal communication.
Key Forms of Non-Verbal Communication:
Body Language: This includes facial expressions, gestures, posture, and the way a person physically positions themselves.
For example:
- Leaning forward can indicate a strong interest.
- Frequently looking away might suggest disinterest or impatience.
Sounds (Paralinguistics): This includes tone of voice, volume, pitch, and speech rate. These vocal elements can greatly affect how a verbal message is received.Demonstrating Knowledge of Various Methods of Communication for class 10
Roles of Non-Verbal Communication:
Non-verbal communication can serve five key roles:
- Repetition – Reinforces and strengthens the verbal message.
- Contradiction – May conflict with the spoken words, suggesting the speaker is being untruthful.
- Substitution – Replaces a verbal message. For instance, a facial expression might express an emotion more clearly than words.
- Complementing – Enhances the verbal message. Example: Praising an employee verbally while giving a pat on the back.
- Highlighting (Accenting) – Emphasizes certain parts of the verbal message. For example, pounding a table can underline the importance of a statement.
Non-Verbal Communication: Body Language and Gestures
Body Language
Body language is a powerful and essential tool that helps people communicate effectively without using words. It includes postures, gestures, and whole-body movements that reveal how a person feels or what they intend to convey. Body language is commonly used in various environments such as schools, offices, industries, and social settings to express ideas, emotions, or attitudes non-verbally.
Key Features of Body Language:
It involves voluntary physical actions of body parts.
It includes movements, especially of the limbs and head.
It does not follow any grammatical rules.
It must be interpreted broadly by the observer, often in context.
Common examples of body language include:
Crossing arms across the chest (defensiveness or discomfort)
Tapping fingers (impatience)
Crossing legs (comfort or relaxation)
Pulling your ear (nervousness or uncertainty)
Putting your head in your hands (frustration or stress)
Sitting up straight (alertness or confidence)
Rubbing your eyes (tiredness or disbelief)
Standing with hands clasped behind your back (confidence or formality)
Facial Expressions
Facial expressions are one of the most universal and immediate forms of non-verbal communication. They reflect a person’s inner emotional state and are easily recognized across cultures.
Through facial expressions, we can communicate emotions such as:
- Happiness – shown by smiling or bright eyes
- Sadness – indicated by a frown or downturned mouth
- Anger – shown through clenched jaws or narrowed eyes
- Fear – revealed by wide eyes or a tense expression
Facial expressions are often instinctive and spontaneous, making them one of the most honest forms of communication.